Abstract family of languages
In computer science, in particular in the field of formal language theory, the term abstract family of languages refers to an abstract mathematical notion generalizing characteristics common to the regular languages, the context-free languages and the recursively enumerable languages, and other families of formal languages studied in the scientific literature.
Contents |
Formal definitions
A formal language is a set 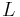 for which there exists a finite set of abstract symbols
for which there exists a finite set of abstract symbols 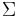 such that
such that 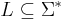 , where * is the Kleene star operation.
, where * is the Kleene star operation.
A family of languages is an ordered pair 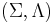 , where
, where
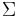 is an infinite set of symbols;
is an infinite set of symbols;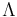 is a set of formal languages;
is a set of formal languages;- For each
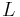 in
in 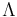 there exists a finite subset
there exists a finite subset 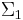 ⊂
⊂ 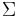 such that
such that 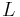 ⊆
⊆ 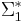 ; and
; and 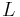 ≠ Ø for some
≠ Ø for some 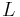 in
in 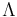 .
.
A trio is a family of languages closed under e-free homomorphism, inverse homomorphism, and intersection with regular language.
A full trio, also called a cone, is a trio closed under arbitrary homomorphism.
A (full) semi-AFL is a (full) trio closed under union.
A (full) AFL is a (full) semi-AFL closed under concatenation and the Kleene plus.
Some families of languages
The following are some simple results from the study of abstract families of languages.[1][2]
Within the Chomsky hierarchy, the regular languages, the context-free languages, and the recursively enumerable languages are all full AFLs. However, the context sensitive languages and the recursive languages are AFLs, but not full AFLs because they are not closed under arbitrary homomorphisms.
The family of regular languages are contained within any cone (full trio). Other categories of abstract families are identifiable by closure under other operations such as shuffle, reversal, or substitution.[3]
Origins
Seymour Ginsburg of the University of Southern California and Sheila Greibach of Harvard University presented the first AFL theory paper at the IEEE Eighth Annual Symposium on Switching and Automata Theory in 1967.[4]
Notes
- ^ Ginsburg (1975)
- ^ Springer, "abstract family of languages"
- ^ Springer, "AFL operations"
- ^ Ginsburg & Greibach (1967)
References
- Ginsburg, Seymour; Greibach, Sheila (1967). "Abstract Families of Languages". Conference Record of 1967 Eighth Annual Symposium on Switching and Automata Theory, 18-20 October 1967, Austin, Texas, USA. IEEE. pp. 128-139.
- Seymour Ginsburg, Algebraic and automata theoretic properties of formal languages, North-Holland, 1975, ISBN 0-7204-2506-9.
- John E. Hopcroft and Jeffrey D. Ullman, Introduction to Automata Theory, Languages, and Computation, Addison-Wesley Publishing, Reading Massachusetts, 1979. ISBN 0-201-029880-X. Chapter 11: Closure properties of families of languages.
- Mateescu, Alexandru; Salomaa, Arto (1997). "Chapter 4: Aspects of Classical Language Theory". In Rozenberg, Grzegorz; Salomaa, Arto. Handbook of Formal Languages. Volume I: Word, language, grammar. Springer-Verlag. pp. 175–252. ISBN 3540614869.